SPRING SALE | Buy 2 Get 1 FREE on all orders placed in May 2020 | Place Order
SPRING SALE | Buy 2 Get 1 FREE on all orders placed in May 2020 | Place Order

SillDry aims to provide our customers with in-depth knowledge on the importance of building protection from water intrusion. As such, we’ve compiled and defined this list of terms related to our product.
ASTM – ASTM International is an international standards body for a broad range of industrial areas, including construction, metals and plastics, paints and coatings, petroleum, textiles, and more. SillDry meets and exceeds ASTM E2112-07 standards for the installation of doors and windows in construction projects.
Building envelope – The elements of a building’s infrastructure that separate the controlled internal environment from external environmental factors.
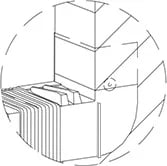
Drainage channels – A channel designed to direct the flow of water outside of the building envelope. SillDry’s design includes drainage channels that move water safely outside the building envelope to prevent damage caused by water intrusion.
Expandable construction – A design element that allows significant expansion without the loss of capability, facilitating compatibility with a broad range of window and door opening sizes.
Flashing (window and door) – A thin waterproofing solution used to mitigate water intrusion into a building envelope by eliminating crevices, gaps, and other spaces where moisture may collect and eventually seep through. Effective flashing relies on gravity and downward-facing seams to ensure that water runs safely outside of the building envelope without pooling.
Flashing tape – A thin and continuous material used to seal openings in a building envelope against infiltration by air, moisture, and other external elements. Of the varying methods used to seal a building envelope, adhesive flashing tape is the most expensive due to high waste, specific labor requirements, and time-sensitive installation that may only be conducted in dry weather with little or no wind.
International Code Council (ICC) – A non-profit association that provides standards, training, and certifications for the construction of affordable, safe, sustainable, and resilient structures. SillDry exceeds the standards set forth in ICC building codes.
International Building Code (IBC) – Regulations regarding the structural integrity and safety of buildings. SillDry exceeds the standards set forth in 2018 IBC Code section 1404.4.
International Residential Code (IRC) – Building codes dictating the safe design and construction of residential buildings. SillDry exceeds the standards set forth in 2018 IRC code section R703.4.
Sill membrane – A solution that fully wraps around a windowsill, including internal and external edges, to prevent water intrusion.
Sill pan – A water intrusion solution typically made from plastic, copper, or high-end metals. Sill pans may be glued, soldered, and cut during construction as necessary to facilitate a proper fit to the building envelope geometry.
Sloped sill pan – A slope is created in the sill pan, either by design or through shimming. The slope creates a pathway for water to drain safely outside of the building envelope.
Smart Accordion Technology® – SillDry’s single-piece, expandable accordion construction provides compatibility with door and window openings from 18 inches up to 12 feet. Smart Accordion Technology drastically reduces the training and skill level required for installation compared to other flashing solutions. See “expandable construction.”
Thermoplastic olefin (TPO) – A strong, waterproof thermoplastic made from a blend of rubber and either polypropylene or high molecular weight polyethylene, as well as a filler to provide reinforcement. SillDry is created from TPO using injection molding, offering durability for all weather types and seasons. Other properties of TPO include high and low temperature tolerances, low thermal conductivity, high UV resistance, and high impact resistance.
Water intrusion – A term referring to water that enters a building envelope due to improper sealing solutions. Water intrusion into a building envelope may weaken structural supports, corrode metal parts, and create optimal conditions for mold and mildew, all of which impact the safety and long-term durability of the entire building.